What Data Can We Extract from Ableton's .als and .asd Files
If you've ever wondered what data Ableton Live stores in its project files, you're not alone. As part of our work at MusicTech Lab, we needed to extract metadata from Ableton projects – tempo, time signature, track names, and song sections – to power our music analysis workflows. The result is MTL Ableton Analyser, an open-source Python tool that parses both .als (Ableton Live Set) and .asd (Ableton Sample Data) files.
In this article, we'll explore what's inside these files and how to extract useful data from them programmatically.
Understanding Ableton's File Formats
Ableton Live uses two primary file formats for storing project and analysis data:
| Format | Full Name | Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
.als | Ableton Live Set | Gzip-compressed XML | Complete project data – tracks, clips, tempo, arrangement |
.asd | Ableton Sample Data | Binary | Analysis cache – detected BPM, warp markers, waveform peaks |
The key insight is that .als files are actually compressed XML, making them relatively straightforward to parse. The .asd files, however, are proprietary binary and require reverse-engineering to extract data.
Data Extractable from .als Files
When you decompress an .als file, you get a well-structured XML document containing the entire project state. Here's what we can reliably extract:
Project Metadata
| Data Point | Description | XML Path |
|---|---|---|
| Tempo (BPM) | Project tempo | .//Tempo/Manual |
| Time Signature | Numerator and denominator | .//TimeSignature/* |
| Track Count | Number of tracks in project | .//Tracks |
| Track Names | User-defined track names | EffectiveName, UserName attributes |
Warp Markers
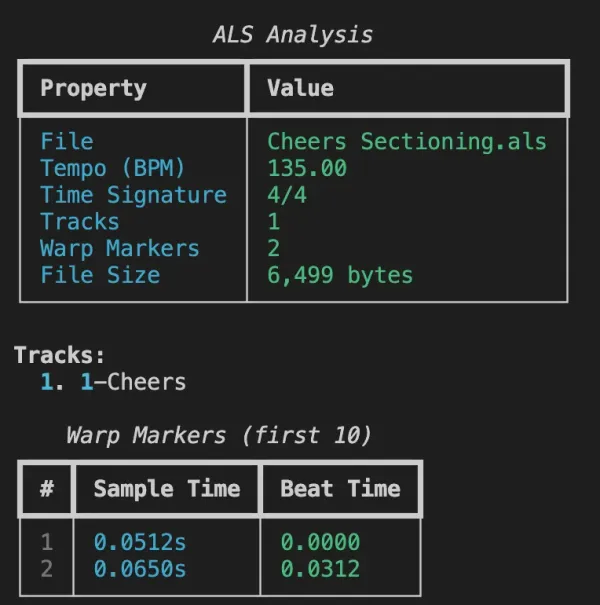
Warp markers define the relationship between audio time (seconds) and musical time (beats). Each marker contains:
- SecTime – Position in the audio file (seconds)
- BeatTime – Corresponding position in beats
This data is essential for beat-synced playback and tempo manipulation.
Locators (Section Markers)
Perhaps the most valuable data for music analysis – locators represent named positions in your arrangement:
{
"sections": [
{ "name": "INT1", "beat": 0 },
{ "name": "VER1", "beat": 32 },
{ "name": "CHO1", "beat": 64 },
{ "name": "BRD1", "beat": 96 },
{ "name": "OUT1", "beat": 128 }
]
}
These locators, when combined with tempo data, give you a complete song structure map with precise timestamps.
Data Extractable from .asd Files
The .asd format is more challenging. Ableton creates these files automatically when you analyze audio, storing:
Detected Metadata
| Data Point | Detection Method | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Format Version | First byte | Typically version 6 |
| Tempo (BPM) | Binary search at known offsets | Ableton's auto-detected BPM |
| Time Signature | Marker string search | Numerator/Denominator extraction |
| Waveform Data | Presence check | Boolean – are peaks pre-computed? |
BPM Detection Strategy
The BPM value in .asd files isn't at a fixed offset. Our parser searches multiple known locations:
KNOWN_BPM_OFFSETS = [7736, 8448, 8632, 7685, 7740, 8440]
def find_bpm(data: bytes) -> Optional[float]:
for offset in KNOWN_BPM_OFFSETS:
if offset + 4 <= len(data):
value = struct.unpack('<f', data[offset:offset+4])[0]
if 60.0 <= value <= 200.0:
return round(value, 2)
# Fallback: scan byte range for valid BPM
return scan_for_bpm(data, range_start=6000, range_end=9500)
.asd files represents Ableton's auto-detection, which may differ from the project tempo in the .als file. The .als tempo is always the authoritative value.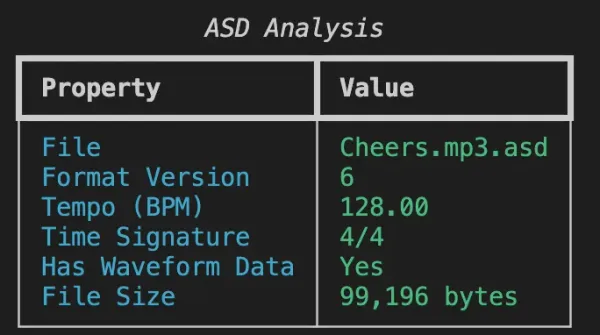
Practical Applications
Waveform Visualization with Sections
By combining data from both file types, we can generate rich visualizations:
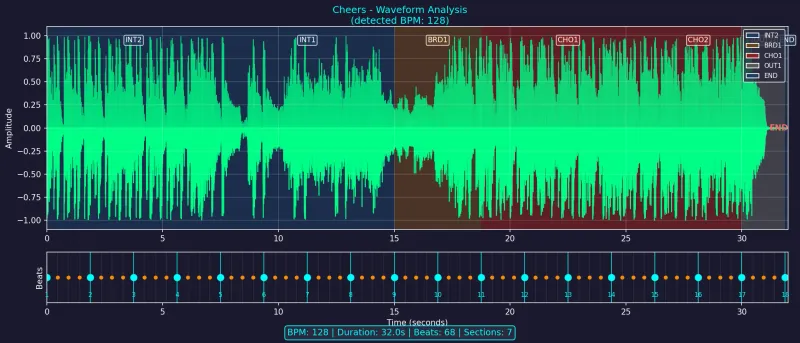
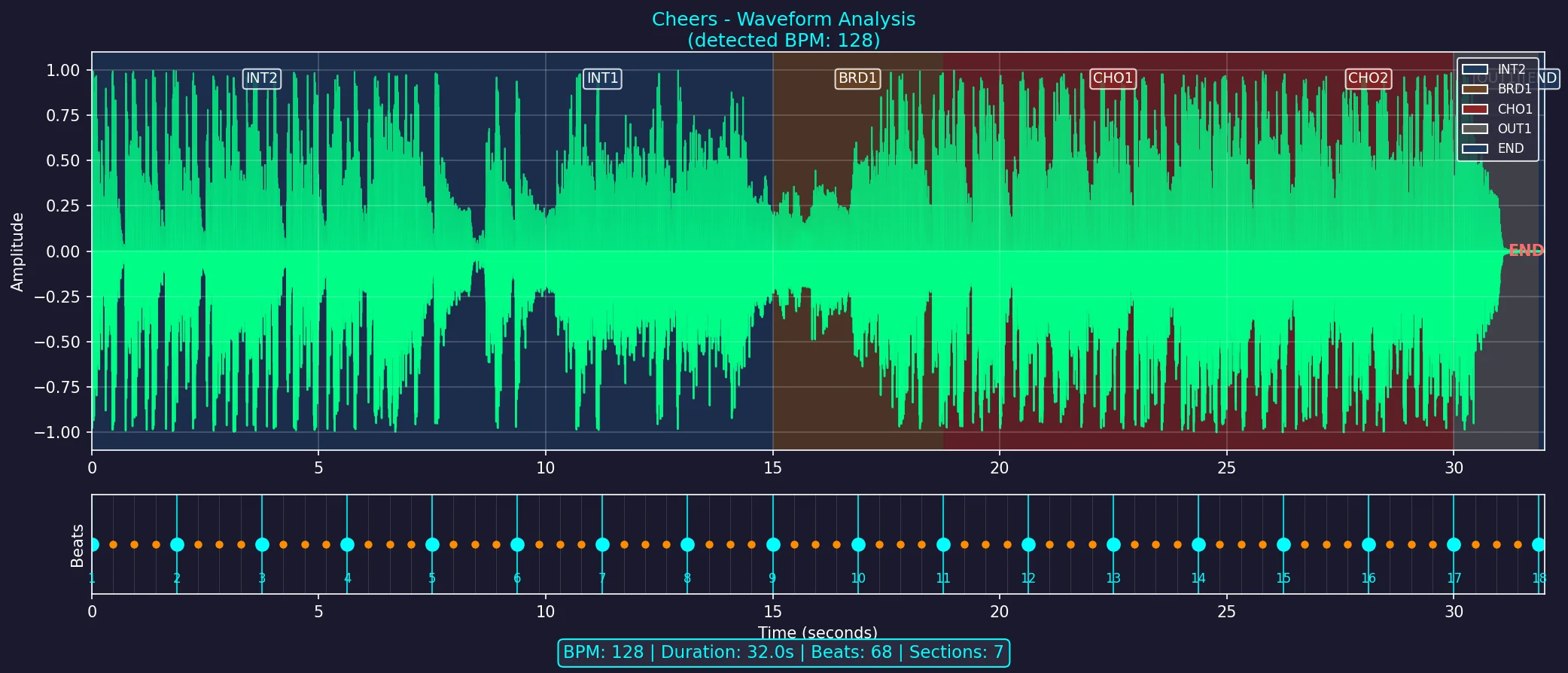
The visualization includes:
- Waveform amplitude – extracted from the audio file
- Beat grid – calculated from BPM and time signature
- Section overlays – color-coded backgrounds from locator data
- Downbeat markers – emphasized beats at bar boundaries
WaveSurfer.js Integration
For web applications, we export a JSON format compatible with WaveSurfer.js:
{
"version": "1.0",
"filename": "track.mp3",
"duration": 180.5,
"sampleRate": 44100,
"bpm": 128,
"beatsPerBar": 4,
"totalBeats": 385,
"peaks": [0.12, 0.45, 0.89, ...],
"beats": [
{ "time": 0.0, "beat": 1, "isDownbeat": true },
{ "time": 0.469, "beat": 2, "isDownbeat": false }
],
"sections": [
{ "name": "INT1", "start": 0.0, "end": 15.0, "color": "#1E3A5F" },
{ "name": "VER1", "start": 15.0, "end": 30.0, "color": "#3D1A5F" }
]
}
This powers interactive, beat-synced waveform players in the browser.
Using MTL Ableton Analyser
The tool is available as an open-source Python CLI:
git clone https://github.com/musictechlab/mtl-ableton-analyser
cd mtl-ableton-analyser
poetry install
Analyze Files
poetry run mtl-ableton-analyser analyze /path/to/project.als --verbose
poetry run mtl-ableton-analyser analyze /path/to/audio.mp3.asd
poetry run mtl-ableton-analyser analyze /path/to/projects --recursive
Generate Visualizations
poetry run mtl-ableton-analyser visualize audio.mp3 --als project.als -o waveform.png
Export for Web
poetry run mtl-ableton-analyser export audio.mp3 --als project.als -o waveform.json
Capabilities Summary
| Capability | .als | .asd | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extract BPM | ✅ Exact | ✅ Detected | .als is authoritative |
| Time Signature | ✅ | ✅ | Both reliable |
| Track Names | ✅ | ❌ | Only in project files |
| Warp Markers | ✅ | ❌ | Beat-to-time mapping |
| Section Markers | ✅ | ❌ | From locators |
| Waveform Presence | ❌ | ✅ | Cache indicator |
| File Size | ✅ | ✅ | Basic metadata |
Limitations
While we can extract a lot, some data remains inaccessible:
- Detailed onset data – Ableton stores transient detection but in an undocumented format
- Embedded waveform peaks – Detected but not directly extractable from
.asd - Plugin states – Complex binary data within the XML
- Write capability – This is a read-only tool
What's Next?
This tool is part of our broader work on music analysis at MusicTech Lab. Combined with our other Ableton integrations, you can build powerful workflows:
- Create section markers in Ableton → Export with our Max for Live device
- Analyze files programmatically → Use MTL Ableton Analyser
- Visualize in web applications → WaveSurfer.js integration
- Enhance with AI → Feed structure data to ML models
Related Articles
- Exporting Ableton Live Locators to JSON with Max for Live – Create and export section markers directly from Ableton
- Connecting Your Max for Live Device to a Cloud API – Send Ableton data to web services
- Automatic Song Structure Analysis – How AI Detects Intro, Verse, and Chorus – AI-powered section detection
- Building a DIY MIDI Controller for Ableton Live with Arduino – Hardware integration with Ableton
Have questions about parsing Ableton files or building music analysis tools? Get in touch – we'd love to hear about your use case.
Need Help with This?
Building something similar or facing technical challenges? We've been there.
Let's talk — no sales pitch, just honest engineering advice.
Exporting Ableton Live Locators to JSON with Max for Live
Build a custom Max for Live device that exports arrangement locators (INTRO, VERSE, CHORUS) along with BPM to a structured JSON format — perfect for integration with external tools and AI-powered music analysis pipelines.
Factors that contribute to the success or failure of an IT outsourcing project
Several factors have an impact on the success or failure of software development outsourcing projects. The knowledge of these factors improves the outsourcing strategy.
